What is onychomycosis
yeast
- Candida albicans (Candida albicans) – most commonly seen on the fingers, is a complication of existing onychomycosis caused by dermatophytes.
- Candidiasis parapsilosis (C. parapsilosis) - affects the nail plate from the edges. The first symptom is the appearance of black spots on the fingertips that gradually grow in size. Candida parapsilosis often completely destroys the nail plate.
Mold
- Scourge - often infects a previously injured big toe.
- Aspergillus or black mold – Only people with low immunity are at risk of contracting onychomycosis. The main symptoms of the disease are deformation of the nail plate and the appearance of normally nourishing blackheads.
- Fusarium - This onychomycosis is very rare because the pathogen lives on crops. It is only possible to infect a person if they have an open wound, scrape or crack on the leg.
dermatophytes
- Trichophyton rubrum (Trichophyton rubrum) - develops on the lateral and distal surfaces. The main symptoms in the early stages of development are yellow spots or white stripes. Without special treatment, fungal spores can spread throughout the body and cause severe skin damage.
- Trichophyton mentagrophytes (Trichophyton mentagrophytes) – Cracks between the toes, severe pain when moving. Without proper treatment, it can spread to the nails; the fungus especially often affects the thumb and little finger.
- Epidermophyton floccosum - in the initial stages it affects the skin of the fingers. Onychomycosis presents as peeling skin on the feet, along with itching and increased sweating on the fingers. If left untreated, epidermophyton can cause atrophy.
What does onychomycosis look like?
- Distal – when only the edges are affected by fungus;
- Lateral - the pathological process begins near the skin ridge;
- Proximal – changes affect the lower part;
- White superficial onychomycosis - White spots or streaks appear.
Regional onychomycosis
normal nutritional type
- increased vulnerability;
- lose luster;
- White or grayish-yellow spots appear on the entire nail surface;
- The bed is visually divided into sections;
- Gray mucus gradually oozes from under the nails.
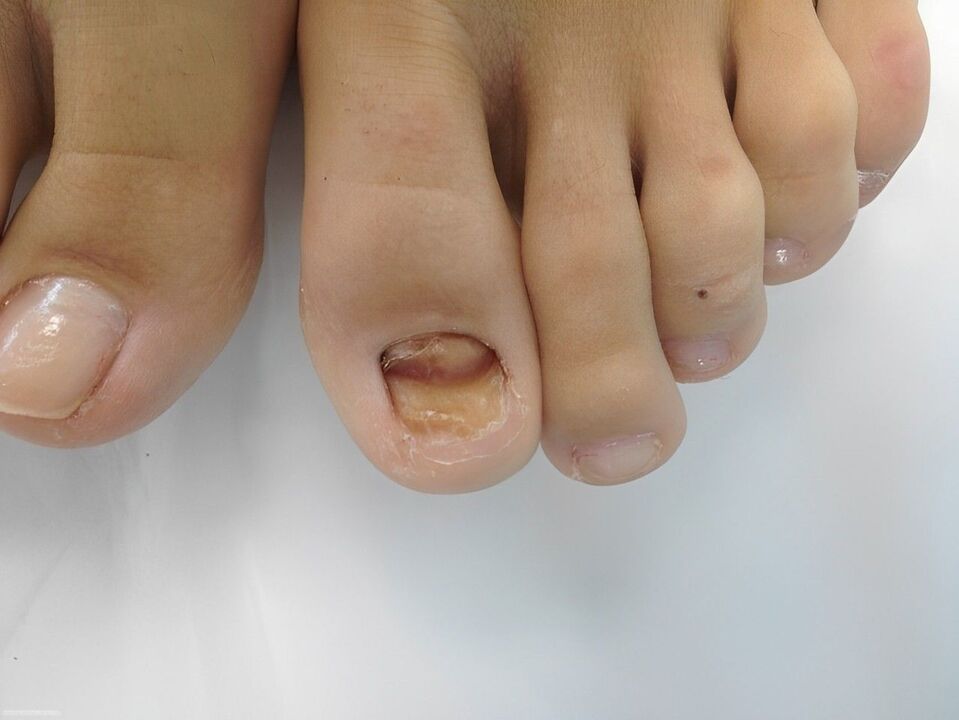
Hypertrophic type
- Gross - Extensive lesions affecting the thickness of the nail plate.
- Horizontal - Appears in side parts.
- Distal - The infection is located beneath the free part of the bed.
white surface morphology
nail stripper
Candida onychomycosis
- Lack of skin along the nail growth line;
- The edges of the boards are brittle and broken;
- Horizontal stripes appear on the bottom of the bed;
- Inflammation of cutaneous ridges;
- Nail plate is tan;
- Soft tissue soreness.
proximal deformation
atrophic
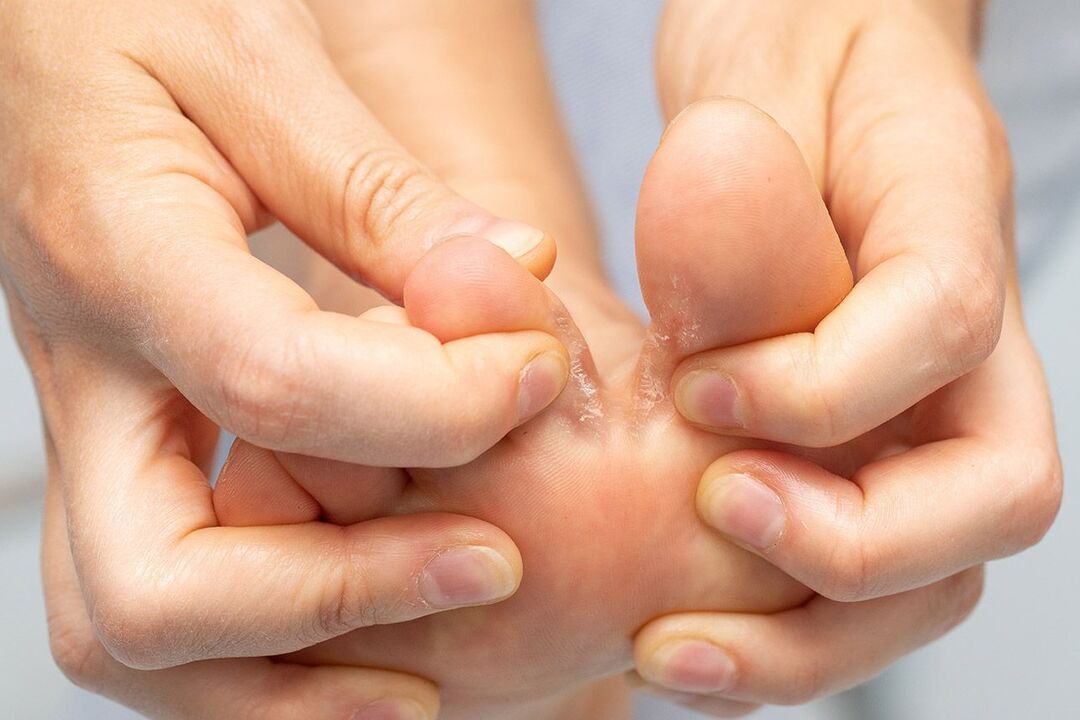
Types and stages of fungal infections
- Onychomycosis is the most common type of fungus. The first signs of fungus appear in the form of small yellow spots on the free edge of the nail. As the disease progresses, the steel plate will become thicker and deeper cracks may form on it, causing discomfort when walking. This form of fungal pathology is difficult to treat.
- White superficial onychomycosis - the pathogenic microorganism affects only the upper layer of the nail. The board does not get thicker, but over time it becomes loose and has a structure similar to chalk. Treatment is not difficult and health will improve quickly.
- Subungual onychomycosis is a rare form of the pathology. Symptoms of the fungus appear as thickening of the skin in the nail fold area and the nail becoming completely white and opaque.
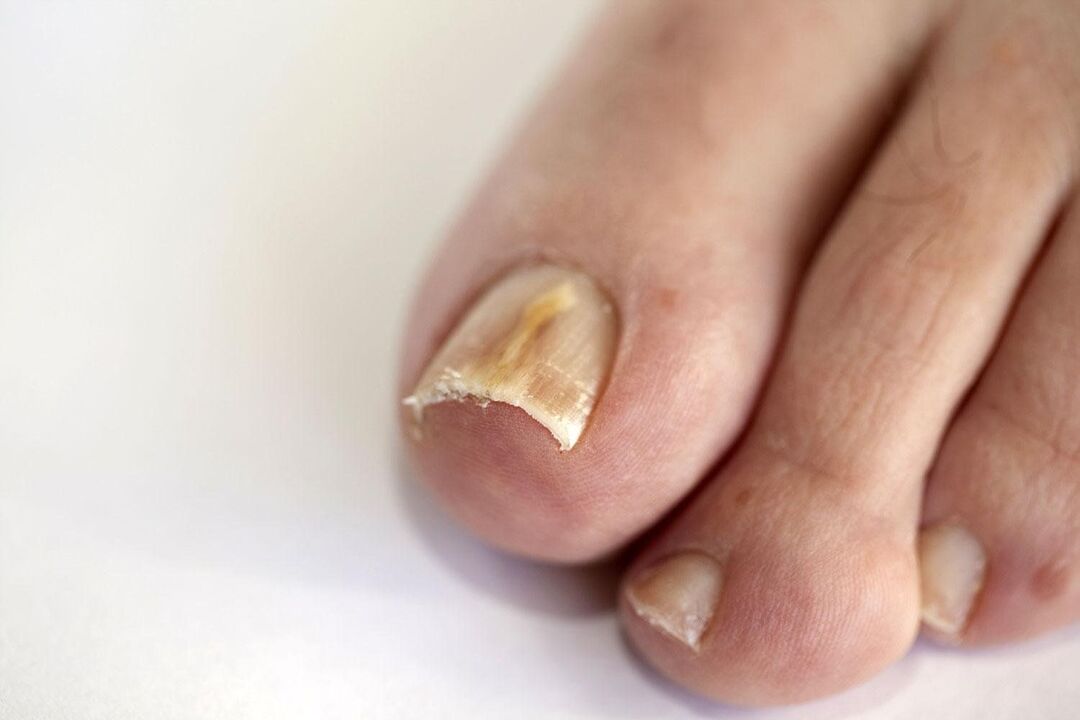
How to Identify Fungus on Toenails - Common Symptoms
- The edge of the plate is yellow, or white inclusions appear near the growth area;
- Deformation - the appearance of waves, knots and other irregularities;
- As the infection progresses, the pads become red, flaky, and swollen;
- Start exfoliating and get out of bed;
- Small cracks may appear between the fingers, and sometimes blisters may appear.
Itching and burning sensation
lose natural color
- The color turns yellow and wrinkles appear. When you try to cut the edge, the tip starts to chip. Occasionally an unpleasant odor may occur.
- The finger completely changed color, became dull and cloudy, and had strange inclusions. The yellow begins to darken, black streaks appear, and green areas may appear. It becomes very difficult to cut the affected nail.
- The entire nail changed - it became noticeably thicker, and it was impossible to trim the edges without softening.
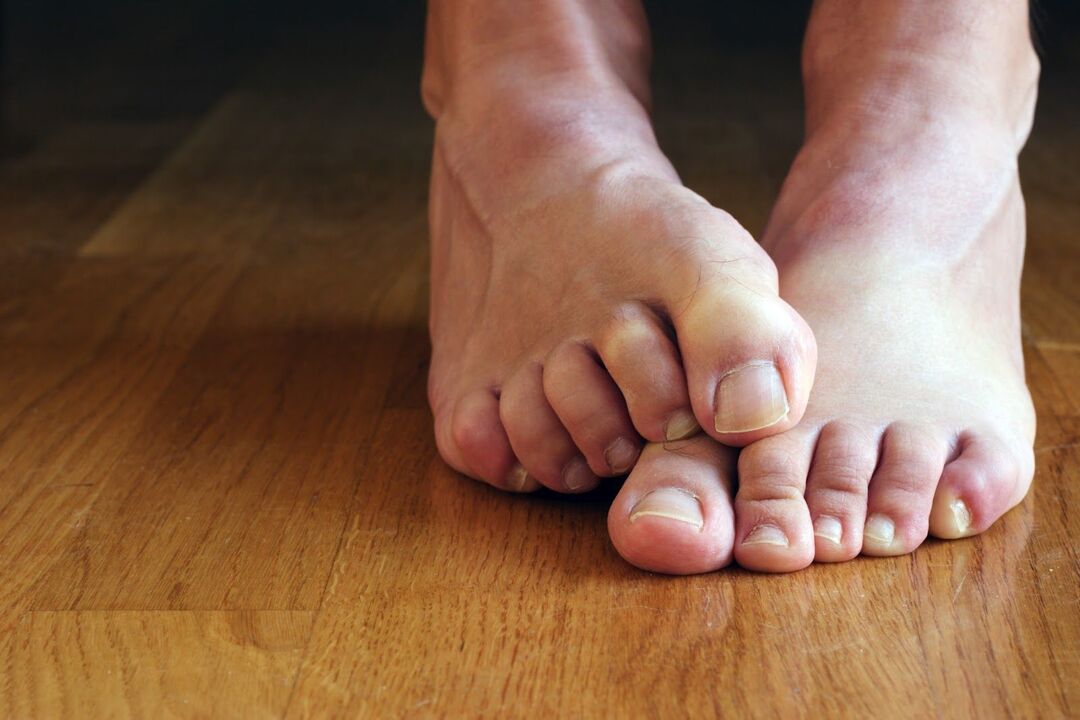

pain in nail area
- As the affected area thickens, it loses its original appearance and becomes deformed. In this case, even the most worn-out shoes can cause significant discomfort when walking. Therefore, the pain will not only bother you while walking, but also after taking off your shoes.
- As the spores spread, the fungus takes over more and more new territory. When an infection enters the soft nail tissue, the infection often affects the nerve endings, causing painful, paroxysmal or throbbing pain. If you develop symptoms as a result, you may experience discomfort even when you are resting.
- One of the symptoms of foot fungus is the development of small cracks and blisters between the toes. The skin may become very red and inflamed, and the fingers may become swollen. Such wounds on the feet heal very slowly and are constantly painful due to the increased sweating in the area between the toes when wearing closed shoes.
How does onychomycosis start?
- Infection with dermatophytes begins at the free edge of the plate. The fungus appears as small yellow spots and a broken surface.
- Yeast-like fungi are characterized by a proximal form - the infection starts at the base. The main symptoms of candidiasis-type onychomycosis are inflammation of the periungual folds, cuticle separation, and pain when pressing.
- Mold turns fingers green, brown, or black. Fungal infections appear as spots, dots, or longitudinal plates.
Symptoms of fungal nail infection
- An unpleasant cloudy tint appears on the surface of the nail plate on the toes;
- The nail plate begins to peel off and separate from the nail bed;
- Affected nails lose their original shape, become thicker and become matted;
- Cracks gradually form between the toes; the patient begins to experience pain in the area of the damaged nail;
- The skin on the toes begins to peel;
- Itchy skin appears between the toes.
What are the dangers of untreated onychomycosis?
- Untreated onychomycosis opens the door to other infections.
- Additionally, fungi can act as allergens and ultimately trigger allergies to nail fungi as an allergen.
- Onychomycosis complicates the course of many diseases, such as diabetes.
- In particularly severe cases, against the background of a long course of illness or weakened immunity, fungal infections can lead to deep-seated mycosis - penetration of the fungus through the blood into the internal organs.
How to get rid of fungus on toenails?
- The first group is local influence means. This group includes medicinal varnishes and peel-off patches, ointments, creams and gels. Most topical medications are only effective in the early stages of the disease.
- The second group consists of oral systemic antifungal drugs. Usually these are capsules or tablets that are fungistatic. They stop the spread of fungal diseases and have long-term effects, significantly reducing the likelihood of another outbreak of the disease.
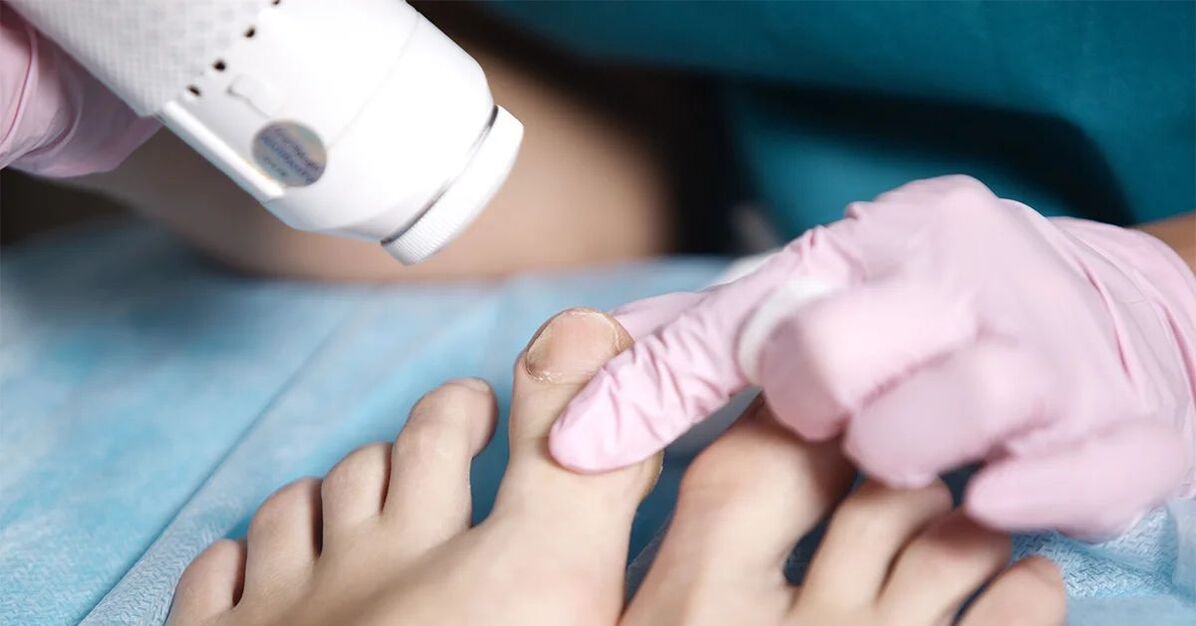
Laser Treatment
- Laser treatment of fungus is considered one of the most effective ways to get rid of this disease.
- Under the influence of the beam, fungal cells die immediately.
- The laser beam does not harm nearby tissue.
- Advanced forms of the fungus can be cured in just four laser treatment procedures.
Drug treatment for onychomycosis
- Degree of plate change;
- Stages of hyperkeratosis;
- damaged area;
- Clinical forms of pathology.
- Using a nail file, carefully work on the nail plate;
- Use antifungals;
- Wrap the nail in a bandage;
- Remove it after a day;
- Use fungal treatments prescribed by your dermatologist.
attention! Antifungal systemic drugs are not used in the initial stages of onychomycosis development.
Treat onychomycosis at home
- Apple cider vinegar . Simply soak your feet in a 1: 1 mixture of apple cider vinegar and warm water for about 15-20 minutes daily. After soaking, let your toenails dry completely (you can use a hair dryer). Within about two weeks, you will notice that the fungus is gone and a beautiful new fungus has replaced the old damaged nail.
- Tea tree oil should be applied to fungal infected skin and nails three times a day. A single dose is 4 to 10 drops of product. This treatment should be continued for at least two weeks, and possibly longer, to ensure the infection does not return. This oil should not be used by children or pregnant women.
- Pass freshly picked celandine through a meat grinder and squeeze out the juice from the resulting pulp (this is done through 3-4 layers of gauze). It should yield approximately 200 ml. Mix the juice with 200 ml. 70% alcohol and leave for 24 hours. The prepared juice is used to lubricate the affected nails, but treatment can only be carried out after the feet have been steamed for 10 minutes and completely dried. The course of treatment lasts for 10-12 days, with 3-4 treatments per day.
- Another way to get rid of onychomycosis is to treat it with iodine at home. this is very simple. Apply iodine to the nail plate every day for three weeks. In this case, regularly remove the growing tip of the damaged nail.
- Kombucha also helps fight fungus. For this treatment, compression is required: wrap a dish of kombucha in cellophane and wrap a bandage on the leg and put on socks. In the morning, you need to wash your feet with warm water, carefully remove the dead spots, and lubricate them with iodine. Side effects include very severe pain, but you can achieve your desired results more quickly.

- Flat feet, congenital or acquired foot deformities;
- Poor blood circulation in the lower limbs;
- Increased sweating of the feet;
- The skin of corns and feet is too rough;
- The deck is often injured;
- Decreased immunity, any chronic disease, diabetes.
Precaution
- Avoid direct contact with fungus carriers.
- Observe personal hygiene regulations and wash hands after going to public places.
- After cleaning, carefully wipe the area between your fingers, as fungus prefers warm, moist conditions.
- Don’t use other people’s shoes and household items.
- Wear socks made from natural fabrics.
- Please wear shoes when in public pools, bathhouses or saunas.
- Use personal manicure accessories.